# Install packages
if (!requireNamespace("data.table", quietly = TRUE)) {
install.packages("data.table")
}
if (!requireNamespace("jsonlite", quietly = TRUE)) {
install.packages("jsonlite")
}
if (!requireNamespace("gggibbous", quietly = TRUE)) {
install.packages("gggibbous")
}
if (!requireNamespace("ggplot2", quietly = TRUE)) {
install.packages("ggplot2")
}
# Load packages
library(data.table)
library(jsonlite)
library(gggibbous)
library(ggplot2)Moon charts
Hiplot website
This page is the tutorial for source code version of the Hiplot Moon charts plugin. You can also use the Hiplot website to achieve no code ploting. For more information please see the following link:
The moon chart is a graph that uses the moon’s waxing and waning to reflect the size of the data.
Setup
System Requirements: Cross-platform (Linux/MacOS/Windows)
Programming language: R
Dependent packages:
data.table;jsonlite;gggibbous;ggplot2
sessioninfo::session_info("attached")─ Session info ───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
setting value
version R version 4.5.2 (2025-10-31)
os Ubuntu 24.04.3 LTS
system x86_64, linux-gnu
ui X11
language (EN)
collate C.UTF-8
ctype C.UTF-8
tz UTC
date 2026-02-03
pandoc 3.1.3 @ /usr/bin/ (via rmarkdown)
quarto 1.8.27 @ /usr/local/bin/quarto
─ Packages ───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
package * version date (UTC) lib source
data.table * 1.18.2.1 2026-01-27 [1] RSPM
gggibbous * 0.1.1 2021-01-06 [1] RSPM
ggplot2 * 4.0.1 2025-11-14 [1] RSPM
jsonlite * 2.0.0 2025-03-27 [1] RSPM
[1] /home/runner/work/_temp/Library
[2] /opt/R/4.5.2/lib/R/site-library
[3] /opt/R/4.5.2/lib/R/library
* ── Packages attached to the search path.
──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────Data Preparation
The loaded data are the name of the restaurant and the number of types of food in the restaurant, the number of decorative style types, the number of tableware sets and the number of price types.
# Load data
data <- data.table::fread(jsonlite::read_json("https://hiplot.cn/ui/basic/moon-charts/data.json")$exampleData$textarea[[1]])
data <- as.data.frame(data)
# Convert data structure
data[, 1] <- factor(data[, 1], levels = unique(data[, 1]))
rest_cols <- colnames(data)[-1]
tidyrest <- reshape(
data,
varying = rest_cols,
v.names = "Score",
timevar = "Category",
times = factor(rest_cols, levels = rest_cols),
idvar = colnames(data)[1],
direction = "long"
)
# View data
head(data) Restaurant Food Decor Service Price
1 Anscombe"s Luncheonette 5 2 4 4
2 Chai Squared 3 5 2 5
3 Tukey"s Honest Southern Diner 4 3 3 2
4 Bagels ANOVA 4 1 3 5
5 Spearmint Row 1 5 5 2Visualization
# Moon charts
p <- ggplot(tidyrest, aes(0, 0)) +
geom_moon(aes(ratio = (Score - 1) / 4), fill = "black") +
geom_moon(aes(ratio = 1 - (Score - 1) / 4), right = FALSE) +
facet_grid(Category ~ Restaurant, switch = "y") +
theme_minimal() +
theme(
panel.grid = element_blank(),
axis.text = element_blank(),
axis.title = element_blank()
)
p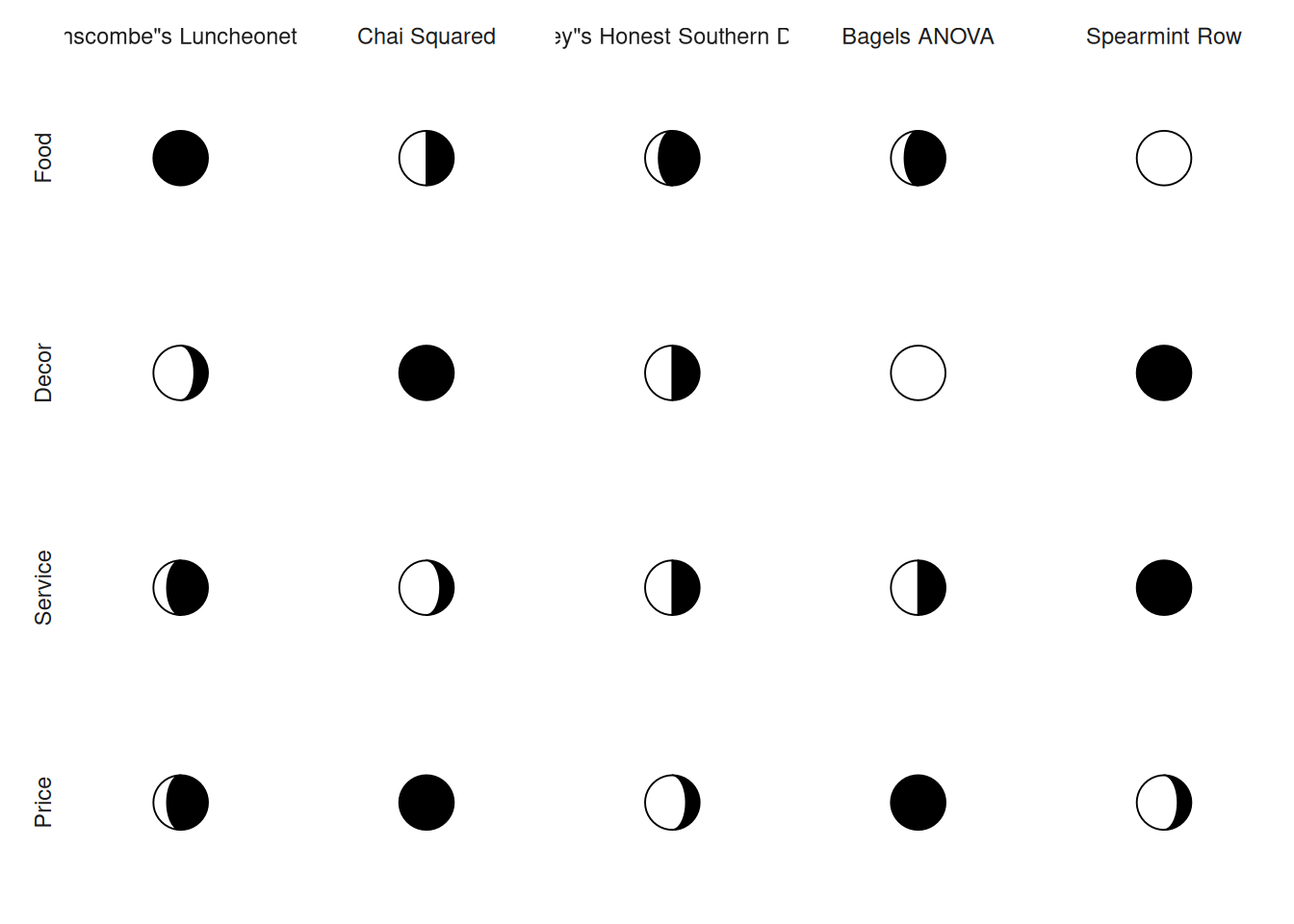
The first row of the diagram shows the name of the restaurant, the first column shows different variables in the restaurant, the blank moon represents the number of 1 (the least number), the black moon represents the number of 5 (the most number) data, as the number of data increases, the black area of the moon gradually becomes larger, that is, gradually becomes full moon.