# Install packages
if (!requireNamespace("calendR", quietly = TRUE)) {
install.packages("calendR")
}
# Load packages
library(calendR)Calend Highlight
Date highlighting marks are mainly used to display changes in data within certain specific date ranges in time series data, and can be used for an overview of activity frequencies and marking of special dates.
Example
Setup
System Requirements: Cross-platform (Linux/MacOS/Windows)
Programming Language: R
Dependencies:
calendR
sessioninfo::session_info("attached")─ Session info ───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
setting value
version R version 4.5.2 (2025-10-31)
os Ubuntu 24.04.3 LTS
system x86_64, linux-gnu
ui X11
language (EN)
collate C.UTF-8
ctype C.UTF-8
tz UTC
date 2026-02-04
pandoc 3.1.3 @ /usr/bin/ (via rmarkdown)
quarto 1.8.27 @ /usr/local/bin/quarto
─ Packages ───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
package * version date (UTC) lib source
calendR * 1.2 2023-10-05 [1] RSPM
[1] /home/runner/work/_temp/Library
[2] /opt/R/4.5.2/lib/R/site-library
[3] /opt/R/4.5.2/lib/R/library
* ── Packages attached to the search path.
──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────Data Preparation
The data is the calendar data for a specified year, and certain date ranges can be selected to be highlighted.
# Construct data
set.seed(1)
data <- rnorm(365)
# View data
head(data)[1] -0.6264538 0.1836433 -0.8356286 1.5952808 0.3295078 -0.8204684Visualization
1. Chinese Calendar
It should be noted that if you are in China, the default weeknames and monthnames are in Chinese; if you are in other countries/regions, the default weeknames and monthnames are in English.
# Chinese Calendar
p <- calendR(
year = 2025,
month = NULL,
from = NULL,
to = NULL,
start = "M",
mbg.col = 2,
# orientation = "portrait",
months.col = "white",
months.pos = 0.5,
monthnames = c(
"一月",
"二月",
"三月",
"四月",
"五月",
"六月",
"七月",
"八月",
"九月",
"十月",
"十一月",
"十二月"
),
weeknames = c("一", "二", "三", "四", "五", "六", "日"),
special.days = data,
special.col = "#00338888",
gradient = TRUE,
low.col = "#FFFFFF88",
font.family = "sans",
font.style = "plain",
day.size = 2,
# ncol = 2,
lunar = FALSE,
pdf = FALSE
)
p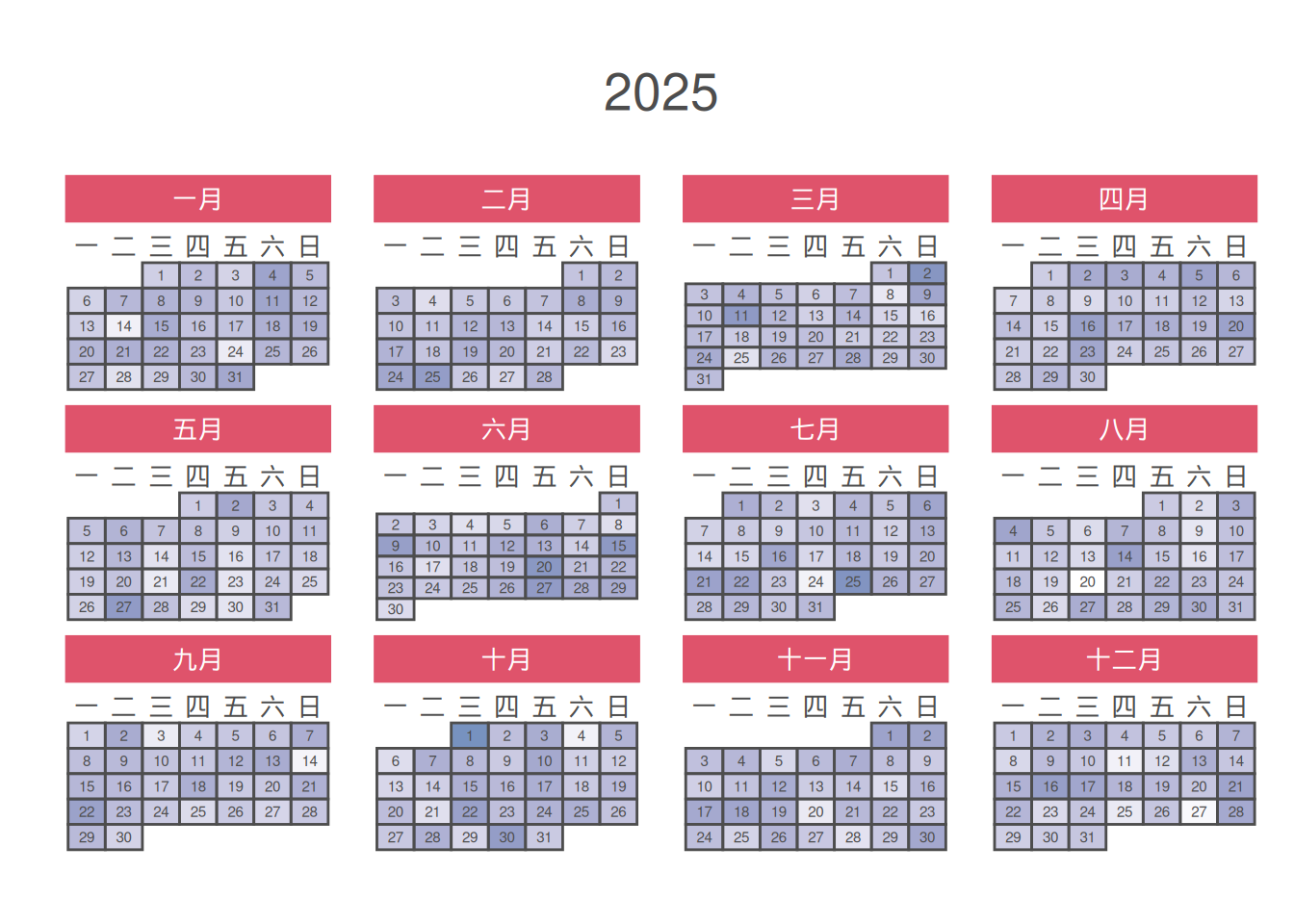
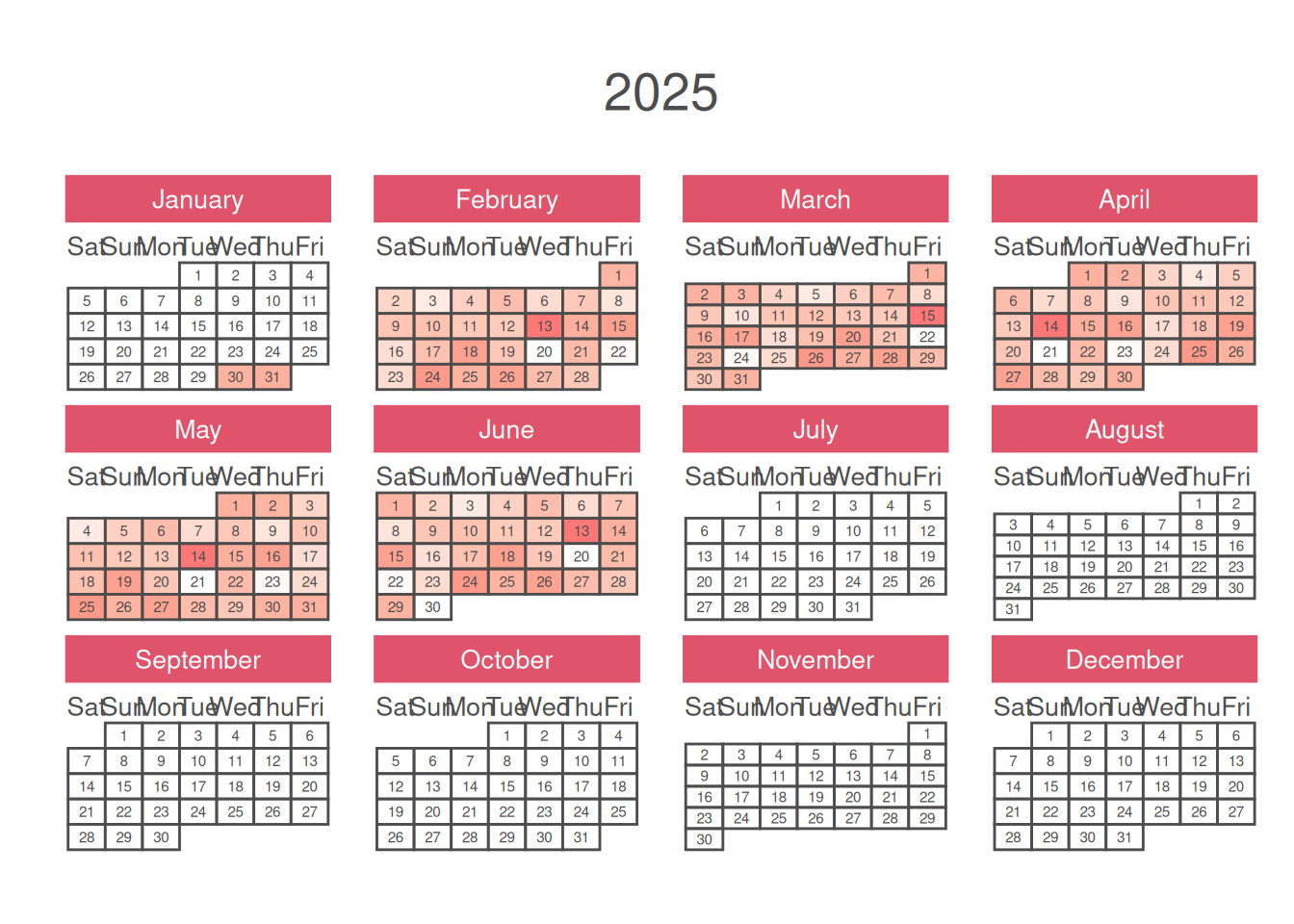
2. English Calendar
# English Calendar
p <- calendR(
year = 2025,
month = NULL,
from = NULL,
to = NULL,
start = "S",
mbg.col = 2,
# orientation = "portrait",
months.col = "white",
months.pos = 0.5,
monthnames = c(
"January",
"February",
"March",
"April",
"May",
"June",
"July",
"August",
"September",
"October",
"November",
"December"
),
weeknames = c("Sun", "Mon", "Tue", "Wed", "Thu", "Fri", "Sat"),
special.days = data,
special.col = "#00888888",
gradient = TRUE,
low.col = "#FFFFFF88",
font.family = "sans",
font.style = "plain",
day.size = 2,
# ncol = 2,
lunar = FALSE,
pdf = FALSE
)
p
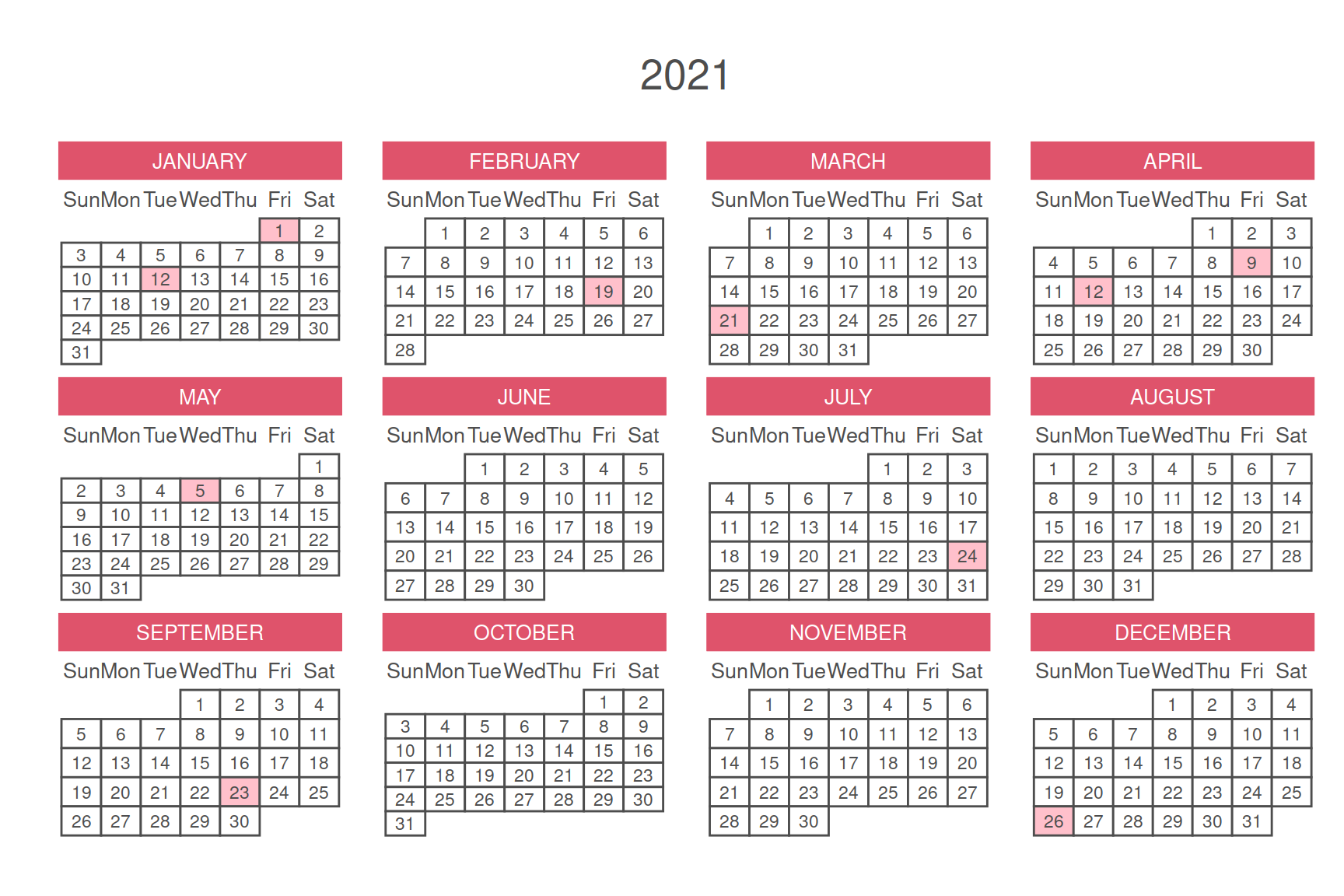
3. Calendar Period
# Calendar Period
data <- rnorm(30, 15, 10)
days <- rep(min(data) - 0.05, 365)
days[30:180] <- data
p <- calendR(
year = 2025,
month = NULL,
from = NULL,
to = NULL,
start = "S",
mbg.col = 2,
# orientation = "portrait",
months.col = "white",
months.pos = 0.5,
monthnames = c(
"January",
"February",
"March",
"April",
"May",
"June",
"July",
"August",
"September",
"October",
"November",
"December"
),
weeknames = c("Sun", "Mon", "Tue", "Wed", "Thu", "Fri", "Sat"),
special.days = days,
special.col = "#FF000088",
gradient = TRUE,
low.col = "#FFFFFF88",
font.family = "sans",
font.style = "plain",
day.size = 2,
# ncol = 2,
lunar = FALSE,
pdf = FALSE
)
p