# 安装包
if (!requireNamespace("sf", quietly = TRUE)) {
install.packages("sf")
}
if (!requireNamespace("rnaturalearth", quietly = TRUE)) {
install.packages("rnaturalearth")
}
if (!requireNamespace("rnaturalearthdata", quietly = TRUE)) {
install.packages("rnaturalearthdata")
}
if (!requireNamespace("gstat", quietly = TRUE)) {
install.packages("gstat")
}
if (!requireNamespace("dplyr", quietly = TRUE)) {
install.packages("dplyr")
}
if (!requireNamespace("ggplot2", quietly = TRUE)) {
install.packages("ggplot2")
}
if (!requireNamespace("ggspatial", quietly = TRUE)) {
install.packages("ggspatial")
}
if (!requireNamespace("ggnewscale", quietly = TRUE)) {
install.packages("ggnewscale")
}
if (!requireNamespace("ggrepel", quietly = TRUE)) {
install.packages("ggrepel")
}
if (!requireNamespace("ggfx", quietly = TRUE)) {
install.packages("ggfx")
}
if (!requireNamespace("doParallel", quietly = TRUE)) {
install.packages("doParallel")
}
if (!requireNamespace("viridis", quietly = TRUE)) {
install.packages("viridis")
}
# 加载包
library(sf)
library(rnaturalearth)
library(rnaturalearthdata)
library(gstat)
library(dplyr)
library(ggplot2)
library(ggspatial)
library(ggnewscale)
library(ggrepel)
library(ggfx)
library(doParallel)
library(viridis)人口图
示例
展示疾病发病率的地理分布,颜色深浅表示发病率高低,地图边界表示行政区划。
环境配置
系统: 跨平台(Linux/MacOS/Windows)
编程语言: R
依赖包:
sf;rnaturalearth;rnaturalearthdata;gstat;dplyr;ggplot2;ggspatial;ggnewscale;ggrepel;ggfx;doParallel;viridis
sessioninfo::session_info("attached")─ Session info ───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
setting value
version R version 4.5.2 (2025-10-31)
os Ubuntu 24.04.3 LTS
system x86_64, linux-gnu
ui X11
language (EN)
collate C.UTF-8
ctype C.UTF-8
tz UTC
date 2026-02-02
pandoc 3.1.3 @ /usr/bin/ (via rmarkdown)
quarto 1.8.27 @ /usr/local/bin/quarto
─ Packages ───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
package * version date (UTC) lib source
doParallel * 1.0.17 2022-02-07 [1] RSPM
dplyr * 1.1.4 2023-11-17 [1] RSPM
foreach * 1.5.2 2022-02-02 [1] RSPM
ggfx * 1.0.3 2025-09-03 [1] RSPM
ggnewscale * 0.5.2 2025-06-20 [1] RSPM
ggplot2 * 4.0.1 2025-11-14 [1] RSPM
ggrepel * 0.9.6 2024-09-07 [1] RSPM
ggspatial * 1.1.10 2025-08-24 [1] RSPM
gstat * 2.1-4 2025-07-10 [1] RSPM
iterators * 1.0.14 2022-02-05 [1] RSPM
rnaturalearth * 1.2.0 2026-01-19 [1] RSPM
rnaturalearthdata * 1.0.0 2024-02-09 [1] RSPM
sf * 1.0-24 2026-01-13 [1] RSPM
viridis * 0.6.5 2024-01-29 [1] RSPM
viridisLite * 0.4.2 2023-05-02 [1] RSPM
[1] /home/runner/work/_temp/Library
[2] /opt/R/4.5.2/lib/R/site-library
[3] /opt/R/4.5.2/lib/R/library
* ── Packages attached to the search path.
──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────数据准备
# 全球地理数据
world <- ne_countries(scale = "medium", returnclass = "sf")
# 模拟流行病学数据
set.seed(123)
world$incidence <- runif(nrow(world), 0, 100) # 随机生成发病率数据可视化
1. 基础绘图
# 全球疾病发病率分布基础地图
p1 <- ggplot(data = world) +
geom_sf(aes(fill = incidence)) +
scale_fill_viridis(option = "C") +
labs(title = "Global Disease Incidence",
fill = "Incidence Rate\n(per 100k)")
p1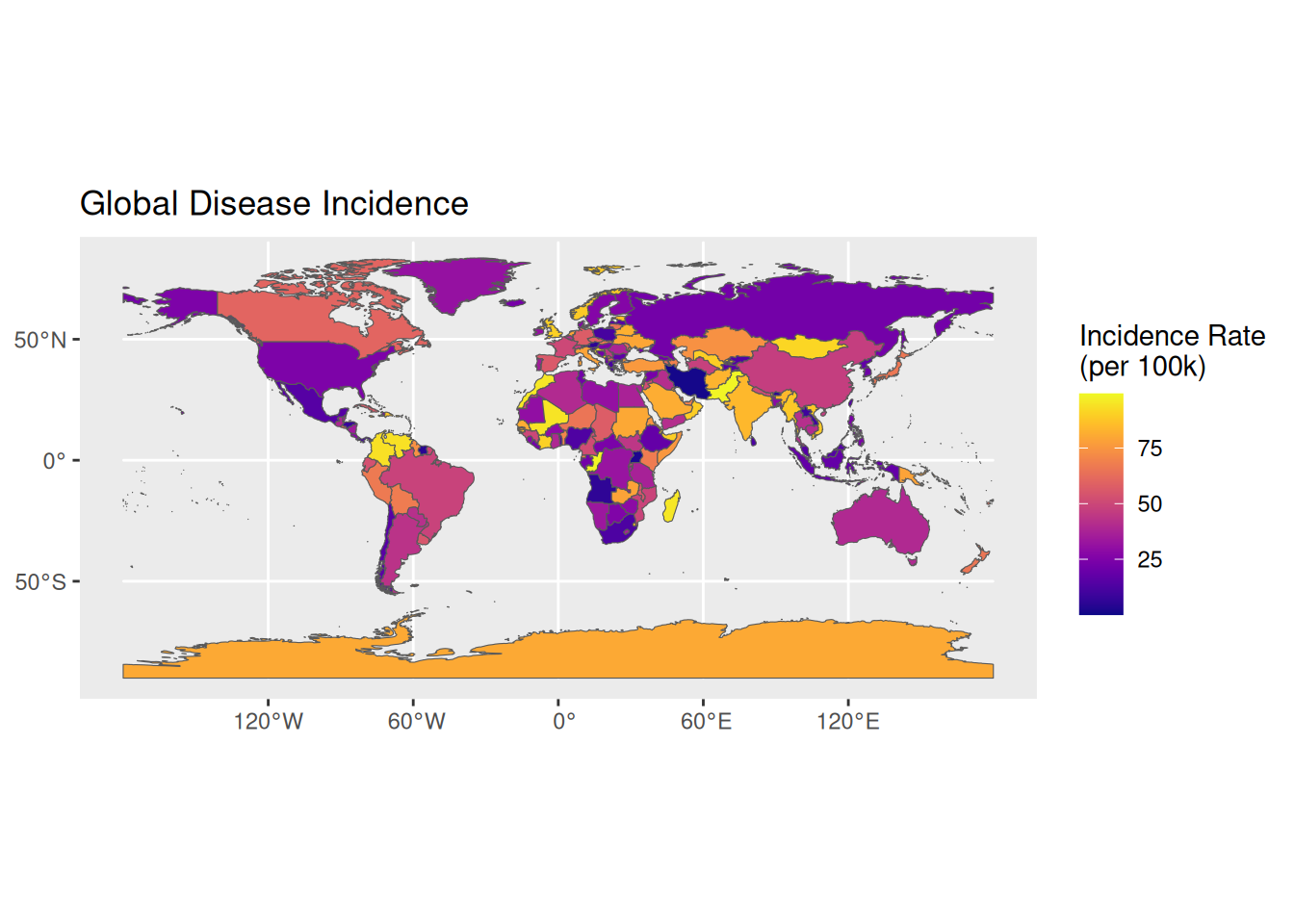
关键参数解析: binwidth / bins aes(fill): 定义颜色映射的流行病学指标
scale_fill_viridis(): 使用无障碍颜色梯度
ne_countries(): 控制地图详细程度的scale参数(small/medium/large)
# 定制化流行病学地图
p2 <- ggplot(data = world) +
geom_sf(aes(fill = incidence), color = "white", size = 0.2) +
scale_fill_gradientn(colors = c("#2c7bb6", "#abd9e9", "#ffffbf", "#fdae61", "#d7191c"),
breaks = c(20, 40, 60, 80)) +
# 比例尺
annotation_scale(
location = "bl",
plot_unit = "km",
style = "ticks",
width_hint = 0.1
) +
# 指北针(修复后)
annotation_north_arrow(
location = "tr",
which_north = "grid", # 使用网格北
style = north_arrow_minimal(
line_width = 1,
text_size = 10
),
pad_x = unit(1.2, "cm"),
pad_y = unit(1.2, "cm")
) +
coord_sf(crs = "+proj=robin",
xlim = c(-1.6e7, 1.6e7),
ylim = c(-7.5e6, 8.5e6),
expand = FALSE) + # 使用罗宾森投影
theme_void() +
guides(fill = guide_colorbar(barwidth = 1)) +
labs(fill = "Incidence Rate")+
theme(
legend.position = c(0.1, 0.3) # 相对位置坐标(左下角为0,0)
)
p2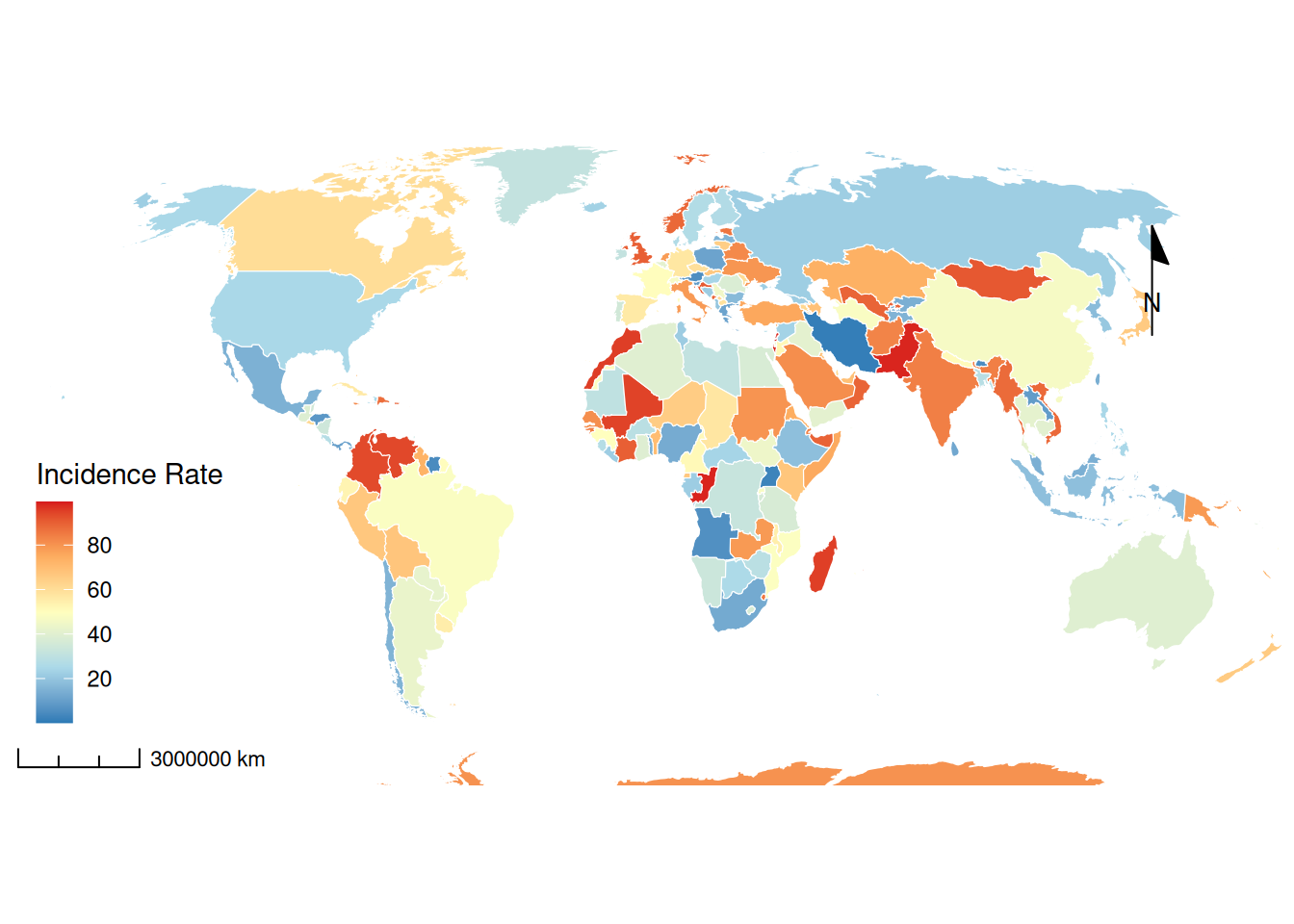
2. 进阶绘图
# 进阶绘图
#进一步处理数据,利用空间点,来推断附近面的情况
#减少计算时间,以下点较少,推算距离越近,分辨率提高,更准确
# 并行初始化
registerDoParallel(cores = 4)
# 数据准备
world_proj <- st_transform(world, "+proj=eqc +units=m")
centroids <- st_centroid(world_proj) %>%
dplyr::select(incidence)
# 创建低分辨率网格(100x100)
grid <- st_make_grid(world_proj, n = c(100,100)) %>%
st_as_sf() %>%
st_join(world_proj, join = st_intersects)
# 变异函数模型优化
variogram_model <- vgm(
psill = 30,
model = "Exp", # 改用指数模型
range = 2e6, # 2000公里相关范围
nugget = 5
)
# 分块并行计算
grid_chunks <- split(grid, cut(st_coordinates(st_centroid(grid))[,1], 4))
krige_result <- foreach(i=1:4, .combine=rbind) %dopar% {
krige(incidence ~ 1,
locations = centroids,
newdata = grid_chunks[[i]],
model = variogram_model,
nmax = 30)
} %>% st_as_sf()
# 转换回WGS84坐标系
krige_result <- st_transform(krige_result, 4326)
advanced_map <- ggplot() +
# 空间插值表面
geom_sf(data = krige_result,
aes(fill = var1.pred, color = var1.pred),
alpha = 0.6) +
scale_fill_gradientn(
colors = c("#2c7bb6", "#abd9e9", "#ffffbf", "#fdae61", "#d7191c"),
name = "Interpolated\nIncidence"
) +
scale_color_gradientn(
colors = c("#2c7bb6", "#abd9e9", "#ffffbf", "#fdae61", "#d7191c"),
guide = "none"
) +
ggnewscale::new_scale_fill() +
# 原始国家边界
geom_sf(data = world,
aes(fill = incidence),
color = "white",
size = 0.1,
alpha = 0.5) +
scale_fill_gradientn(
colors = c("#2c7bb6", "#abd9e9", "#ffffbf", "#fdae61", "#d7191c"),
name = "Country\nIncidence",
breaks = seq(0, 100, 20)
) +
# 3D浮雕效果
ggfx::with_shadow(
geom_sf(data = world,
aes(geometry = geometry),
color = "grey30",
fill = NA,
size = 0.2),
sigma = 5,
x_offset = 3,
y_offset = 3
) +
# 热点标注
geom_sf(data = world %>% filter(incidence > quantile(incidence, 0.9)),
color = "red",
fill = NA,
size = 0.5) +
ggrepel::geom_label_repel(
data = world %>% filter(incidence > quantile(incidence, 0.9)),
aes(label = name, geometry = geometry),
stat = "sf_coordinates",
size = 2.5,
box.padding = 0.2,
min.segment.length = 0,
fill = alpha("white", 0.8)
) +
# 地图元素
annotation_north_arrow(
location = "tr",
width = unit(1.2, "cm"), # 新增宽度参数
height = unit(1.2, "cm"), # 新增高度参数
style = north_arrow_minimal() # 移除尺寸参数
) +
# 坐标投影
coord_sf(crs = "+proj=robin") +
# 主题设置
theme_void() +
theme(
legend.position = c(0.12, 0.3),
legend.background = element_rect(fill = alpha("white", 0.8), color = NA),
plot.title = element_text(hjust = 0.5, face = "bold", size = 16),
panel.background = element_rect(fill = "#F0F8FF")
) +
labs(title = "Advanced Spatial Distribution of Disease Incidence")
advanced_map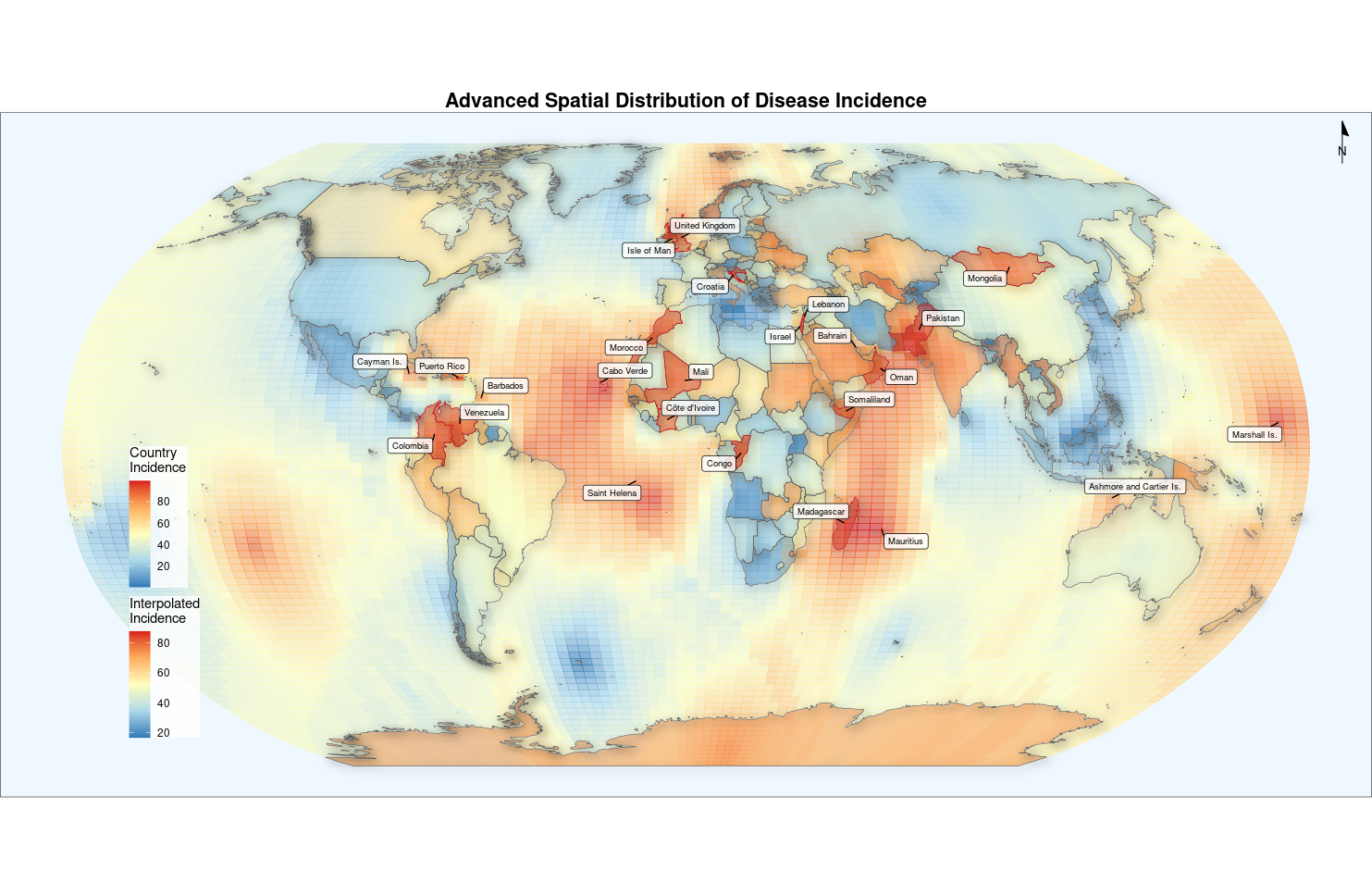
如果你有需要的话可以选择使用callout-tip添加对参数的详细描述。
应用
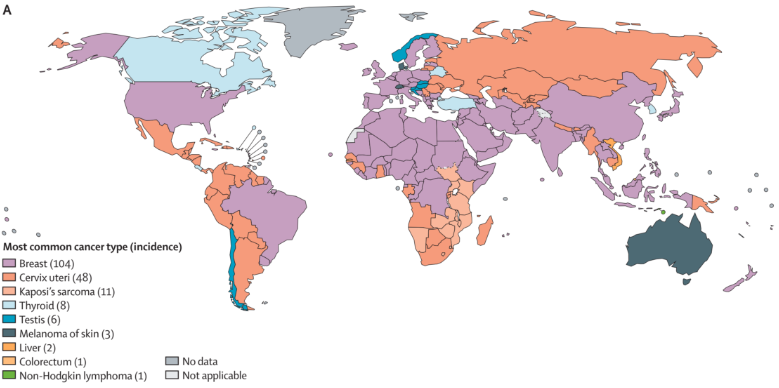
人口图应用
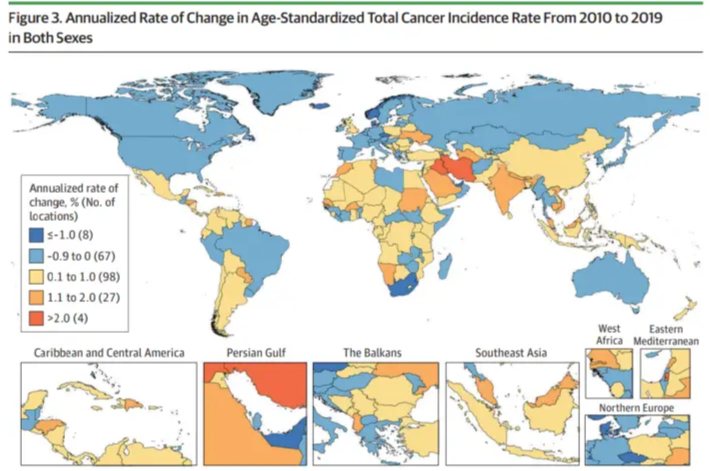
该图显示了全球各国常见肿瘤的差异。 [1]
参考资料
[1] Global Burden of Disease 2019 Cancer Collaboration; Kocarnik JM, Compton K, Dean FE, et al. Cancer Incidence, Mortality, Years of Life Lost, Years Lived With Disability, and Disability-Adjusted Life Years for 29 Cancer Groups From 2010 to 2019: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. JAMA Oncol. 2022;8(3):420-444. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaoncol.2021.6987
[2] Fidler MM, Gupta S, Soerjomataram I, Ferlay J, Steliarova-Foucher E, Bray F. Cancer incidence and mortality among young adults aged 20-39 years worldwide in 2012: a population-based study. Lancet Oncol. 2017;18(12):1579-1589. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(17)30677-0
[3] Wickham H, Chang W, Henry L, et al. ggplot2: Create Elegant Data Visualisations Using the Grammar of Graphics [Computer software]. (Version 3.4.0). 2022. https://ggplot2.tidyverse.org/reference/ggsf.html